does autoclaving kill viruses|industrial autoclave vs medical : company How does an autoclave kill microorganisms? Discover the intricate process behind this powerful sterilization method that ensures safety. Call Us: (02) . viral particles are also effectively inactivated by autoclaving. This includes enveloped viruses like HIV and non-enveloped viruses like norovirus, which are otherwise challenging to eradicate. An autoclave is a machine that uses steam under pressure to kill harmful bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores on items that are placed inside a pressure vessel. The items are .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Many of these difficulties can be avoided if the technique of Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is used for the manufacture of near net shape manifold sections with integral branches and branch .
industrial autoclave vs medical
how to use optical refractometer
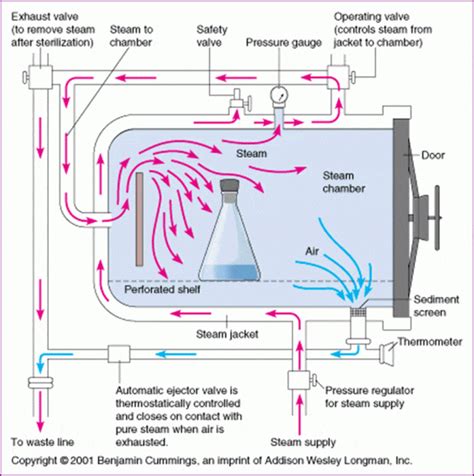
The basic principle of steam sterilization, as accomplished in an autoclave, is to expose each item to direct steam contact at the required temperature and pressure for the specified time. Thus, there are four parameters of steam sterilization: steam, pressure, . The autoclave works by heating the chamber above the boiling point of water, resulting in superheated steam. In this article, we will focus on how does an autoclave kill microorganisms exploring how autoclaves work and why they are so effective at eradicating bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms. Steam sterilization to kill viruses is very effective at hospitals — but it's not necessarily a great option for people's homes. . Even if you had an autoclave on your kitchen counter, using it to deactivate coronavirus would be excessive. The hospital-grade sterilization machines can tackle even the toughest bacteria — like varieties . How does an autoclave kill microorganisms? Discover the intricate process behind this powerful sterilization method that ensures safety. Call Us: (02) . viral particles are also effectively inactivated by autoclaving. This includes enveloped viruses like HIV and non-enveloped viruses like norovirus, which are otherwise challenging to eradicate.
What is autoclaving and why does a healthcare facility need an autoclave? Autoclaving is a sterilization process that uses high-pressure steam at high temperatures to kill bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms that could cause infections. Medical settings are extremely susceptible to the spread of infections and diseases, which is .
The major process types include moist heat by steam autoclaving, ethylene oxide gas, and dry heat. . bacterial spores are the most difficult form of microorganisms to inactivate or "kill" (6). . some alcohols, and glutaraldehyde. Viruses do differ in their susceptibility to lipophilic germicides. These compounds have an affinity for lipid .An autoclave (also called an autoclave machine or autoclave sterilizer) uses high temperature steam and pressure to kill microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungus and spores that are found on items (like surgical or dental equipment) that . An autoclave is a machine that uses steam under pressure to sterilize materials by killing bacteria, viruses, and spores. Autoclave Pressure and Temperature Chart. STERILIZER TEMPERATURE PRESSURE TIME; Steam autoclave: 121°C (250°F) 15 psi: 15 min: Unwrapped items: 132°C (270°F) 30 psi: . How does autoclaving kill bacteria?Do not allow bags to touch the interior walls of the autoclave to avoid melting of plastic. Ensure sufficient liquid is packed with contents of autoclave bags if dry. Place soiled glassware and lab ware in secondary containers and autoclave them in the solids cycle. Do not fill containers more than 2/3 full with liquids.
Microorganisms growing on an agar plate. Sterilization (British English: sterilisation) refers to any process that removes, kills, or deactivates all forms of life (particularly microorganisms such as fungi, bacteria, spores, and unicellular eukaryotic organisms) and other biological agents (such as prions or viruses) present in or on a specific surface, object, or fluid. [1]
Autoclaving is the use of pressurized steam and high temperature to kill microbes, spores, or viruses that are hard to destroy using conventional disinfection methods. Autoclaves can be found in .Autoclaving. Steam sterilisation (ie vacuum steam autoclaving), is the preferred method of sterilising equipment as it is quick, automated, easy to use, reliable, non-toxic and always effective when used correctly. It is particularly suitable for reusable, heat-stable items, so long as these parts are already physically clean.Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a severe global health burden, with approximately 2 billion infected individuals and more than 250 million carriers worldwide. Despite the availability of vaccines and therapeutics, chronic hepatitis B remains incurable. The virus is highly contagious and can circulate with 108 to 1010 infectious particles in a patient’s blood. Because HBV has a very low .
autoclave disinfection
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Aseptic method that destroys pathogens but does not kill spores and viruses, Equipment using steam under pressure, Device used to ensure that an article has been sterilized in an autoclave and more. Autoclaving uses saturated steam under pressure (approximately 15 psi) to achieve a temperature in the autoclave of at least 121° C (25° F). Autoclaving can be used to destroy vegetative bacteria, bacterial spores, and viruses.A similar parameter, the thermal death time (TDT), is the length of time needed to kill all microorganisms in a sample at a given temperature. These parameters are often used to describe sterilization procedures that use high heat, such as autoclaving. Boiling is one of the oldest methods of moist-heat control of microbes, and it is typically . Bacteriophages are viruses that infect bacteria and are used for medical purposes since the early 1900s 1.Despite early successes, phage therapies, i.e., curing bacterial infections with phages .
In a recent study – which looked at whether UVC could be used to disinfect PPE – the authors found that, while it is possible to kill the virus this way, in one experiment it needed the .
Do not sterilize waterproof or water-resistant materials like oil or powders. Do not overcrowd the autoclave with the vessel and equipment. Only use autoclavable bags to autoclave packages wastes. Use autoclavable bags to sterilize your equipment. Do not use aluminum foils. Do not fill the autoclave chamber up to the lid.How Does an Autoclave Work? Autoclaves are machines used in hospitals to clean medical tools. Inside, there’s a special chamber where the tools go. Making sure the autoclave works well involves three important things: time, heat, and the quality of the steam. . It’s important to use autoclaves to kill off any bacteria or viruses in .
In the food industry, high-pressure processing (also called pascalization) is used to kill bacteria, yeast, molds, parasites, and viruses in foods while maintaining food quality and extending shelf life. The application of high pressure between 100 and 800 MPa (sea level atmospheric pressure is about 0.1 MPa) is sufficient to kill vegetative .Why is autoclaving rather than boiling water used for sterilization? Autoclaving uses dry heat instead of water. Boiling water is too hot and may denature proteins. Boiling water does not kill everything, including bacterial endospores and some protozoan cysts. Autoclaving is much faster than boiling water. An autoclave is majorly used for sterilization purposes. Sterilization refers to killing tiny microbes that might be present in any container like bacteria, fungi, spores, viruses, germs, etc. In biotechnology, the Autoclave is widely used to sterilize equipment like glassware and media. It was invented by Charles Chamber in 1879.Therefore, to prevent prion-caused iatrogenic diseases, the use of appropriate procedures to inactivate prions is important. For examples, alcohol treatment, autoclave (121˚C, 20 min) and γ-ray irradiation, which are used for disinfection, antisepsis or sterilization of viruses and bacteria, are not effective against prion.
How do you use an autoclave? Once the chamber is sealed, all the air is removed from it either by a simple vacuum pump (in a design called pre-vacuum) or by pumping in steam to force the air out of the way (an alternative design called gravity displacement).Next, steam is pumped through the chamber at a higher pressure than normal atmospheric pressure so it . Endospore-forming bacteria are ubiquitous, and their endospores can be present in food, in domestic animals, and on contaminated surfaces. Many spore-forming bacteria have been used in biotechnological applications, while others are human pathogens responsible for a wide range of critical clinical infections. Due to their resistant properties, it is challenging to .
The sterilization process kills bacteria, viruses and bacterial spores. Biological indicators and lethality calculations can be used to validate a cycle for an autoclave. Can the process fail? It can, for a variety of reasons. Read on to learn why and what to do in such a circumstance. What to Do if an Autoclave Fails. An autoclave can be .What is autoclaving and why does a healthcare facility need an autoclave? Autoclaving is a sterilization process that uses high-pressure steam at high temperatures to kill bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms that could cause infections. Medical settings are extremely susceptible to the spread of infections and diseases, which is .

Gient Integrated Autoclave with Shredder MWI-300 is an ideal solution for medical waste treatment in hospital. In MWI-300 the shredding and sterilization processes are enclosed in one vessel, the whole treatment process is .
does autoclaving kill viruses|industrial autoclave vs medical